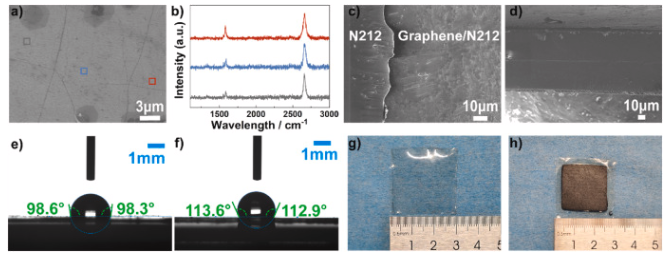
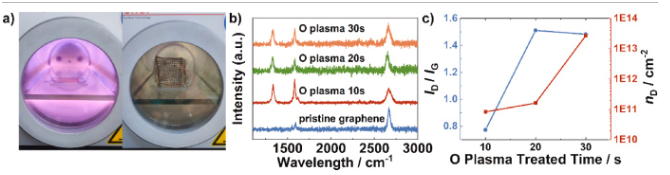
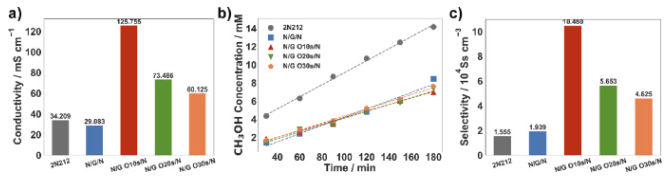
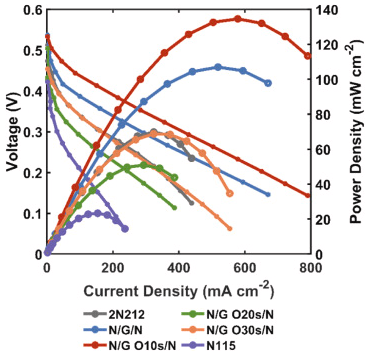
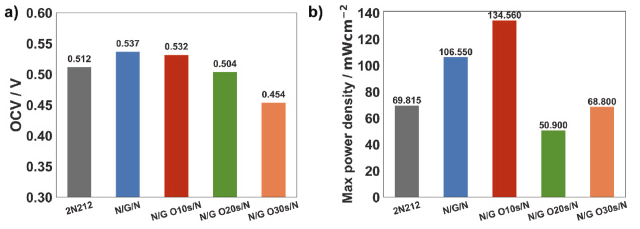
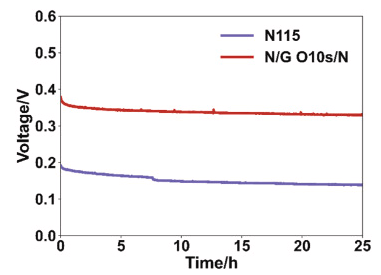
成果简介 直接甲醇燃料电池(DMFC)相比氢燃料电池具有更简单的燃料系统,且在便携式和小型化电源领域展现出广阔应用前景。然而,商业化Nafion膜的甲醇渗透问题会在阴极产生混合电位,导致开路电压(OCV)降低及整体性能下降。尽管将单层石墨烯引入Nafion膜可缓解甲醇渗透并提升OCV,但往往会牺牲质子导电性。本文,西安交通大学史乐教授团队在《Journal of Power Sources》期刊发表名为“Breaking the conductivity-selectivity trade-off in direct methanol fuel cells using oxygen plasma-treated monolayer graphene”的论文,研究将氧等离子体处理的单层石墨烯嵌入Nafion膜中,可同时提升质子导电性和选择性。 这种双重提升使DMFC性能较商业Nafion膜提升92.74%,功率输出分别为60℃时的134.56 mW cm−2和90℃时的254.84 mW cm−2。分子动力学模拟表明,通过等离子体处理引入的含氧功能基团形成了纳米孔,增强了石墨烯与Nafion之间的界面亲和力,从而改善了界面处的水分分布和质子传导。这种方法有效打破了导电性与选择性之间的权衡关系,为提升DMFC性能提供了可行解决方案。 图文导读 图1. Schematic of the synthesis of Nafion/nanoporous graphene/Nafion. a) CVD graphene on copper substrate (centimeter scale, actual size 3 × 3 cm2); b) plasma treatment on copper substrate; c) D520 spin-coating; d) N212 hot-press; e) copper etching in FeCl3; f) air-dried nanoporous graphene on N212; g) another D520 spin-coating on the graphene side; h) another N212 hot-press (actual size 3 × 3 cm2). 图2. Characterization of CVD graphene and the composite N/G/N membrane. a) SEM of graphene on SiO2/Si, rectangles indicate the areas for Raman characterization in b); b) Raman spectra of graphene on SiO2/Si substrate; c) SEM of graphene on N212; d) cross section SEM of N/G/N membrane; e) contact angle of N212; f) contact angle of N212 with graphene transferred; g) photograph of the composited N/G/N membrane; h) photograph of the composited MEA. 图3. Characterization of the perforated graphene. a) photograph of the plasma treating process (left: Ar 20W; right: O2 7W with homemade Faraday cage); b) Raman spectra of perforated graphene; c) Defect density analysis from the Raman spectra in b). 图4. Membrane performance of N212/nanoporous graphene/N212 composite membranes. a) proton conductivity, b) CH3OH permeation, c) selectivity of proton over CH3OH. 图5. Polarization curve of N212/nanoporous graphene/N212 composite membranes in 60 °C DMFC. 图6. Fuel cell performance comparison of N212/nanoporous graphene/N212 composite membranes. 图7. Voltage degradation of best-performed N/G O10 s/N and commercial N115 at 0.08 mA cm−2, 60 °C. 图8. Water distribution analysis at the interfacial regions of Nafion/nanoporous graphene/Nafion composite membranes (grey dots indicate the position of graphene layer). a1, a2) bulk Nafion (λ = 20); b1, b2) Nafion/pristine graphene/Nafion; c1, c2) Nafion/H decorated nanoporous graphene/Nafion; d1, d2) Nafion/epoxy decorated nanoporous graphene/Nafion; e1, e2) Nafion/hydroxyl decorated nanoporous graphene/Nafion; f) Layer-to-layer distribution functions analysis between atoms in water molecule and graphene; g) Layer-to-layer distribution functions analysis between atoms in Nafion and graphene. 小结 一系列夹层结构的Nafion/等离子体穿孔石墨烯/Nafion质子交换膜被合成,以保持对甲醇穿透的显著阻抗,同时克服由原始石墨烯的高质子渗透屏障引起的性能限制。引入氧等离子体穿孔石墨烯后,质子导电率较原始石墨烯膜提高了超过三倍。在燃料电池测试中,N/G O10 s/N膜在开路电压(OCV)方面优于商业N212膜,并实现了最大功率密度92.74%的提升。这一改进归因于质子导电性的提升,同时保留了石墨烯对甲醇的选择性。等离子体穿孔不仅在原始石墨烯中引入选择性纳米孔,通过更大孔径提升质子导电性,还在纳米孔边缘添加功能基团,影响邻近水分布情况。氧等离子体可引入羟基促进质子渗透。然而,延长氧等离子体处理时间会导致羟基转化为环氧基团,反而阻碍质子渗透。这一现象导致石墨烯等离子体处理时间延长时性能下降。因此,适当的时间控制至关重要。根据我们的实验结果,采用法拉第笼进行6秒氩等离子体处理和10秒氧等离子体处理可实现最佳燃料电池性能。这项工作为在DMFCs中应用纳米孔单层石墨烯作为新一代质子交换膜铺平了道路。 文献: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jpowsour.2025.237800
免责声明:本网站所转载的文字、图片与视频资料版权归原创作者所有,如果涉及侵权,请第一时间联系本网删除。

官方微信
《腐蚀与防护网电子期刊》征订启事
- 投稿联系:编辑部
- 电话:010-62316606
- 邮箱:fsfhzy666@163.com
- 腐蚀与防护网官方QQ群:140808414